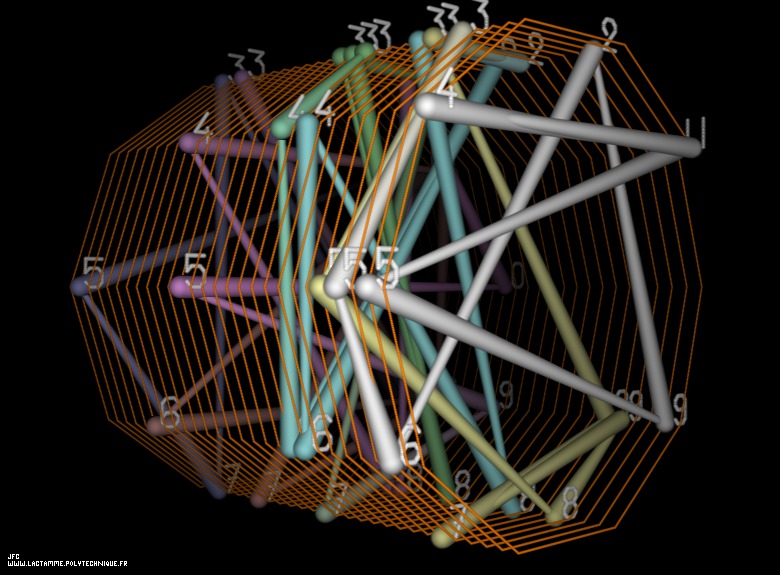
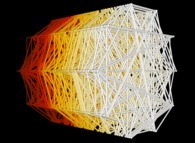
The 50 first digits {141592...} of 'pi' displayed on an helix -orange- [Les 50 premières décimales {141592...} de 'pi' visualisées sur une hélice -orange-].

The 50 first digits {141592...} of 'pi' displayed on an helix -orange- [Les 50 premières décimales {141592...} de 'pi' visualisées sur une hélice -orange-].
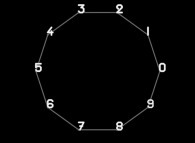 To each digit D inside [0,9] is associated an angle A(D) with the following rule:
To each digit D inside [0,9] is associated an angle A(D) with the following rule:
A(D) = D.(2.pi/10)Then each digit D(n) (n ∈ [1,...]) is displayed as a point (belonging to an helix) with the following tridimensional coordinates:
X = cos(A(D(n)))
Y = sin(A(D(n)))
Z = f(n)
'f' denoting an "arbitrary" function.
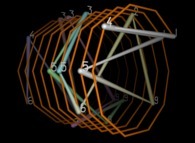
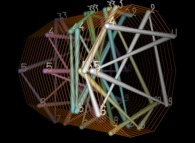
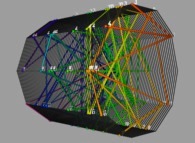
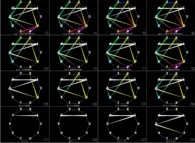 At last, the current picture displays all the segments {D(n),D(n+1)} (for n=1 to 999).
At last, the current picture displays all the segments {D(n),D(n+1)} (for n=1 to 999).
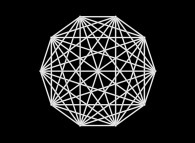

 pi. | 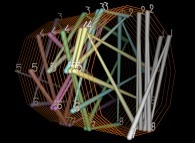 e. | 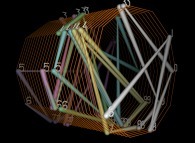 The Golden Ratio. | 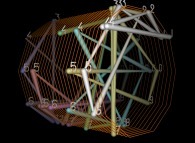 The square root of 2. | 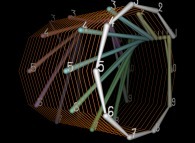 Champernowne number. |